Introduction
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels over an extended period. It affects millions of people globally and poses significant challenges to both individuals and healthcare systems. However, amidst these challenges, there is hope – the possibility of reversing diabetes. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the game-changing strategies that have the potential to reverse diabetes and transform lives.

Table of Contents
Types of Diabetes
Understanding the various types of diabetes is crucial for tailoring effective reversal strategies. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes is more common and often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, and sedentary behavior. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and requires careful management to prevent complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
While genetics play a role in diabetes predisposition, lifestyle factors significantly influence its development. Obesity, unhealthy dietary habits, lack of physical activity, and stress contribute to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism. Additionally, factors such as age, ethnicity, and family history may increase the risk of developing diabetes.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of diabetes is essential for early detection and intervention. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. However, some individuals may experience no symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease. Long-term complications of diabetes include cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve problems, and vision loss.
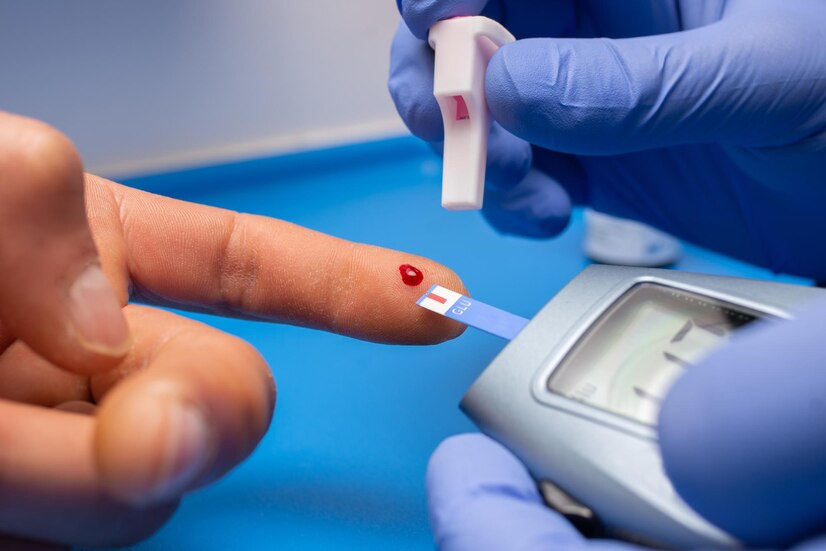
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Diabetes is diagnosed through various blood tests that measure glucose levels. Fasting blood sugar tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, and A1C tests are commonly used diagnostic tools. Additionally, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems provide real-time data on blood sugar levels, allowing for more precise management of diabetes.
Conventional Treatment Options
Conventional diabetes treatments focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the underlying causes of the disease. Medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin may be prescribed to control blood sugar levels. However, these medications do not reverse diabetes and may have side effects. Insulin therapy is essential for individuals with Type 1 diabetes to replace the insulin their bodies cannot produce.
Understanding Reversal
Reversing diabetes involves more than just controlling blood sugar levels; it requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the root causes of the disease. Unlike conventional treatments that focus solely on symptom management, reversal strategies aim to restore normal glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. This may involve dietary changes, increased physical activity, stress management techniques, and other lifestyle modifications.
Dietary Strategies
Diet plays a significant role in diabetes reversal. Low-carbohydrate diets, such as the ketogenic diet, have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and promote weight loss. The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, is also beneficial for blood sugar control and cardiovascular health. Intermittent fasting, which involves cycling between periods of fasting and eating, can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote metabolic health.
Physical Activity and Exercise
Regular exercise is essential for diabetes reversal as it helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and promote weight loss. Aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming are beneficial for cardiovascular health and blood sugar control. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting and resistance training, help build muscle mass and improve metabolic function.
Stress Management and Mental Health
Chronic stress can exacerbate diabetes symptoms and hinder the reversal process. Stress triggers the release of hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which raise blood sugar levels and contribute to insulin resistance. Techniques for managing stress include deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, tai chi, and progressive muscle relaxation. Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional can also help alleviate stress and improve overall well-being.
Sleep and Diabetes Reversal
Quality sleep is essential for metabolic health and diabetes reversal. Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep duration have been linked to insulin resistance, weight gain, and poor blood sugar control. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a conducive sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime can improve sleep quality and support overall health.
Supplements and Alternative Therapies
Certain supplements and alternative therapies may complement conventional treatments and support the reversal process. Chromium, a mineral found in foods such as broccoli, barley, and oats, has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. Cinnamon, a spice with antioxidant properties, may also help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Berberine, a compound found in several plants, has been studied for its potential benefits in diabetes management, including blood sugar control and weight loss. Other natural remedies such as alpha-lipoic acid, fenugreek, and bitter melon may also have beneficial effects on blood sugar metabolism.
Monitoring Progress
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, A1C levels, and weight management is essential for tracking progress and adjusting treatment plans as needed. Keeping a journal of food intake, exercise habits, stress levels, and sleep patterns can provide valuable insights into the factors influencing diabetes reversal. Working closely with healthcare providers, diabetes educators, and nutritionists
FAQs related to diabetes reversal
- Can diabetes be reversed completely?
- While complete reversal may not be possible for everyone, significant improvements in blood sugar control and overall health are achievable with lifestyle modifications and proper management.
- Are there any risks associated with reversing diabetes?
- As with any significant lifestyle changes, there may be risks and challenges involved in reversing diabetes. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to monitor progress and address any potential complications.
- How long does it take to reverse diabetes?
- The timeline for reversing diabetes varies from person to person and depends on factors such as the severity of the condition, adherence to treatment plans, and individual response to interventions. In general, significant improvements can be seen within a few months to a year.
- What role does medication play in diabetes reversal?
- While medications such as metformin and insulin may be necessary for managing blood sugar levels, they are not typically considered primary tools for reversing diabetes. Instead, lifestyle modifications and dietary changes are the main focus of reversal strategies.
- Is diabetes reversal sustainable in the long term?
- Sustainable diabetes reversal requires ongoing commitment to healthy habits and lifestyle choices. By maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, managing stress, and monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can sustain the benefits of diabetes reversal over the long term.
You

1 thought on “Diabetes Reversed: Game-Changing Strategies”